ACELLULAR: not made up or divided by cells
AMOEBOCYTE: cells with pseudopods, located in teh mesohyl; used in processing food, distributing nutrients to other cells and for other functions
BENTHAL: relating to or happening under a body of water on the bottom
BLASTULA: an early stage of embryonic development in animals; produced by cleavage of a fertalized ovum and consisting fo a spherical layer of cells surrounding a fluid-filled cavity
CALCEREA: calcerous sponges; skeleton composed of calcium carbonate
CHOANOCYTES: cells lining the interior body walls of sponges; also known as collar cells
DEMOSPONGIAE: horn sponges (ie. bath sponges); skeleton composed of protein fibers
DIPLONTIC LIFE CYCLE: organism is diploid as an adult
GEMMULE: a bud or fragment produced during the asexual reproduction of sponges
HERMAPHRODITE: an organism possessing both male and female reproductive organs
HEXACTINELLIDA: glass sponges; skeleton composed of silicon dioxide
INTERTIDAL ZONE: the area in marine aquatic environments between the low and high tide marks
INVERTEBRATE: an animal without a backbone
MESOHYL: an acellular gel layer that makes up the innermost layer of a sponge's body
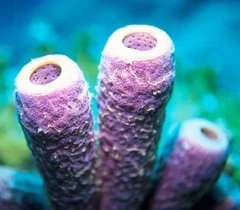
OSCULUM: a large hole at the top of a sponge that expels water and wastes
OSTIA: surface pores on a sponge
OVOCYTE: a cell found in sponges that produces ova
PLANKTON: a diverse group of minute animals and plants that freely drift in water
PORIFERA: the scientific name for sea sponges; means "pore-bearing"
SPICULES: the small needle-like skeletal parts of sponges
SPONGIN: the organic matter composing the skeleton of sponges
Saturday, February 10, 2007
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)

No comments:
Post a Comment